Stages of a Tooth Abscess: Understanding the Journey from Pain to Recovery
The Journey of a Tooth Abscess: Key Stages and Symptoms to Watch For
A tooth abscess is a serious dental condition that occurs when an infection forms at the root of a tooth or in the gums. Understanding the tooth abscess stages is crucial for maintaining your dental health, as it allows you to recognise early signs, take preventive action, and seek treatment before the infection spreads or causes irreversible damage. Whether it’s caused by untreated cavities, gum disease, or a dental injury, the progression of a tooth abscess can vary, and knowing how it develops is key to protecting your smile.
What is a Tooth Abscess?

A tooth abscess is a localised infection that occurs at the root of a tooth or in the gums surrounding it. It typically results from untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or injury, leading to a buildup of pus. The infection can cause significant discomfort and may spread to other areas of the body if not treated promptly.
Early diagnosis and treatment of a tooth abscess are crucial in preventing serious complications, such as tooth loss or the spread of infection to other areas, including the jaw or bloodstream. If left untreated, the infection can worsen, leading to more severe health risks.
Some of the common presenting symptoms of a tooth abscess include:
- Pain when biting down or chewing
- Constant toothache
- Throbbing pain that occurs spontaneously
- Localised swelling in the jaw or cheek
- A “different” feeling when biting
- A “pimple” on the gum next to the tooth
Common signs and symptoms of a tooth abscess include persistent tooth pain, swelling in the gums, sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, a foul taste or smell in the mouth, and fever. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek dental care as soon as possible to address the infection before it progresses.
What Causes an Abscessed Tooth?
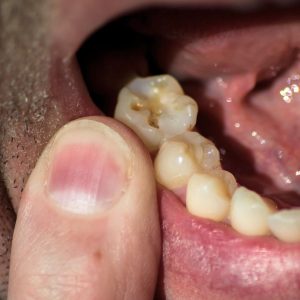
An abscessed tooth is typically caused by a bacterial infection that enters the tooth through a cavity, crack, or other forms of damage to the tooth enamel. Poor dental hygiene, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, can lead to the buildup of plaque and bacteria, increasing the risk of tooth decay. As bacteria penetrate deeper into the tooth, they can infect the pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth, leading to inflammation and pus formation. Additionally, untreated gum disease can contribute to the development of a periodontal abscess, as bacteria infect the tissues surrounding the tooth. Trauma to the tooth, such as a physical injury or unfinished dental work, can also make the tooth more vulnerable to infection and abscess formation. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene are essential for preventing abscesses and maintaining overall dental health.
Types of Tooth Abscesses
Tooth abscesses can occur in different areas of the mouth, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. The location of the abscess plays a crucial role in determining the symptoms, severity, and the appropriate treatment. The three main types of tooth abscesses are:
Gingival Abscess
A gingival abscess is located in the gum tissue, sometimes around a tooth that has experienced an injury or trauma. This type of abscess is typically less severe than the others, as it doesn’t usually affect the tooth’s root. Symptoms of a gingival abscess often include localised pain and swelling around the gum, and it may appear as a small, painful bump or pimple on the gumline. Treatment usually involves draining the abscess and addressing any infection in the gums.
Periodontal Tooth Abscess
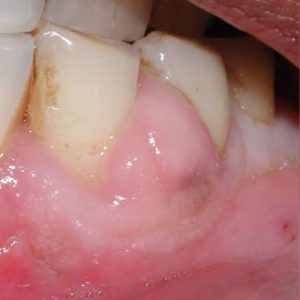
Periapical Abscess
A periapical abscess occurs at the tip of the tooth root, where the infection affects the pulp inside the tooth. This type of abscess is often the result of untreated tooth decay or trauma that allows bacteria to reach the pulp. A periapical abscess can cause severe pain, swelling, and sensitivity, often extending to the jaw or neck. In many cases, the tooth may need to be treated with a root canal to remove the infection and preserve the tooth, or in more severe cases, extraction may be necessary if the infection is too advanced.
The location of the abscess directly impacts the treatment process. A gingival abscess may require only localised care, while a periodontal or periapical abscess may require more extensive procedures, such as a root canal, surgical intervention, or tooth extraction. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for effectively managing the abscess and preventing the infection from spreading further.
How Do I Know If I Have a Tooth Abscess?

Recognising the signs of a tooth abscess early can help prevent the infection from spreading and causing further complications. Common symptoms of a tooth abscess include:
- Pain: A constant, throbbing toothache or sharp pain, which often worsens when chewing or biting down, is one of the most common symptoms. Sometimes the patient can get sinus or generalised jaw pain.
- Swelling: You may notice swelling in the gums, jaw, or cheek, which could be tender to touch and may worsen over time.
- Fever: As the infection progresses, you may experience a mild to moderate fever, indicating that your body is fighting the infection.
- Bad Taste in the Mouth: Pus from the abscess may drain into the mouth, resulting in a foul taste or unpleasant odour.
Different types of tooth abscesses present with varying symptoms, depending on their location:
- Gingival Abscess: This type of abscess is typically characterised by pain and swelling around the gumline, often appearing as a small, tender bump. It may not affect the tooth itself, and the pain is usually more localised.
- Periodontal Abscess: A periodontal abscess often presents with more severe pain, deep gum swelling, and sometimes pus drainage. You may also experience sensitivity in the affected tooth or a “different” sensation when biting, as the infection may extend into the tooth-supporting tissues.
- Periapical Abscess: The pain associated with a periapical abscess is typically sharp and may be radiating, affecting the entire tooth and possibly extending to the jaw or neck. This abscess may cause more intense pain, especially when pressure is applied, and it may cause the tooth to become loose. Swelling in the gum near the root of the tooth and fever can also occur.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek dental care as soon as possible. The stages of a tooth abscess can progress quite quickly without intervention. Early diagnosis and treatment of a tooth abscess can help prevent further complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Tooth Abscess Stages
Understanding the stages of a tooth abscess is crucial for recognising its progression and preventing severe damage to your dental health. The “tooth abscess stages” refer to the various stages of infection, from the initial decay to potential tooth loss. Here’s a breakdown of the typical progression:
Enamel Decay
The first stage of a tooth abscess begins with enamel decay. Enamel, the hard outer layer of the tooth, is the first to be affected by bacteria. This early stage may cause small cavities or areas of discolouration. While enamel decay is usually not painful, it’s a sign that oral hygiene may be compromised, and bacteria are beginning to break down the tooth surface.
Dentin Decay
As the infection progresses, dentin decay sets in. The dentin is the layer beneath the enamel and is much more sensitive. When bacteria invade the dentin, it can cause sharp, intense pain, or sensitivity to hot and cold foods especially when eating or drinking. At this stage, the infection continues to spread deeper into the tooth, and the risk of further damage increases. Be aware though – it can also be completely symptom free!
Tooth Pulp Infection
Next, the infection reaches the tooth pulp, which is the soft tissue inside the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels. This stage of the tooth abscess is characterised by severe pain, often described as throbbing or constant. The infection in the pulp can lead to the death of the nerve, causing the tooth to become discoloured and sensitive to hot and cold temperatures. The pulp infection is often the trigger for the formation of an abscess.
Abscess Formation
Once the infection spreads to the root tip, abscess formation occurs. This stage is marked by the formation of a pus-filled pocket at the root of the tooth. The abscess may cause swelling in the gums, jaw, or cheek, and a foul taste in the mouth due to pus draining. The infection may also lead to fever, and the tooth can feel loose or painful when touched.
Tooth Loss
If left untreated, a tooth abscess can progress to the point where the infection destroys the surrounding bone structure. At this stage, tooth loss is possible. The tooth may either fall out on its own or require extraction due to the damage caused by the abscess. Without intervention, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious health risks; even death.
Understanding the tooth abscess stages can help you identify potential issues early, ensuring timely treatment and preventing the more serious consequences of tooth loss and further infection. If you notice any symptoms of a tooth abscess, it’s essential to consult with your dentist as soon as possible to avoid complications.
How Quickly Does a Tooth Abscess Progress?
The speed at which a tooth abscess progresses can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the infection. However, the stages of a tooth abscess can typically develop over a period of weeks to months . If not addressed, the infection can escalate quickly, spreading from the enamel layer to the deeper tissues of the tooth, and even into the surrounding bone and gums.

Early Stages
In the early stages of a tooth abscess, the infection may be minimal and not always noticeable. The initial enamel decay may not cause pain, and you may only notice slight sensitivity to hot or cold. Dentin decay, which follows, often brings with it more noticeable discomfort, but it can still be managed with dental care and treatment.
Progression to Infection
Once the infection reaches the tooth pulp, you may experience more severe symptoms, such as throbbing pain, especially when chewing or when pressure is applied to the tooth. At this stage, the infection can progress rapidly to form an abscess at the root tip, leading to localised swelling and more intense pain.
Risk of Spreading
If the abscess is left untreated, the infection can spread to nearby tissues, such as the jawbone, or even cause systemic issues, like a fever or swollen lymph nodes. This can result in further complications that may require more invasive treatment, including root canal therapy or tooth extraction. Left untreated, abscesses also have the potential to cause extreme infections, like endocarditis (a bacterial infection of the heart), which can result in death.
Why Early Intervention is Key
The earlier a tooth abscess is diagnosed, the more manageable it will be. In its early stages, a tooth abscess can typically be treated with antibiotics or dental procedures, such as a root canal, to remove the infection. If it reaches the abscess stage, more intensive treatment may be required to prevent the infection from spreading and to save the tooth.
By understanding how quickly a tooth abscess can progress, you can take action to seek treatment sooner, minimising the risk of complications and ensuring better outcomes for your dental health.
How Do I Know if My Tooth Abscess is Spreading?
When a tooth abscess begins to spread, it often presents with more severe symptoms. It’s crucial to recognise these signs early, as untreated abscesses can lead to serious health complications. Recognising these signs can suggest the stages of a tooth abscess have progressed, and that you should seek professional intervention.
Symptoms of a Tooth Abscess Indicating Spread:

- Increased Pain: If the pain from your abscess becomes more intense, particularly if it’s throbbing or radiating to other areas, this could indicate that the infection is worsening or spreading.
- Swelling: Localised swelling around the infected tooth may become more pronounced. The swelling might also spread to the jaw, face, or neck, indicating that the infection is affecting more tissue.
- Fever: A high temperature, often accompanied by chills, is a common sign of infection spreading. It suggests that your body is fighting off the infection, but it also means the infection could be becoming more serious.
- Pain Radiating to Other Areas: If you experience pain extending beyond the infected tooth—such as into your ear, sinus, or neck—it’s a clear indication that the infection is moving to other areas and is no longer confined to the tooth.
Why Untreated Abscesses Are Dangerous
When a tooth abscess goes untreated, the bacteria causing the infection can spread beyond the root of the tooth and into the surrounding tissues. This can result in severe consequences, including:
- Systemic Infection: If the infection enters the bloodstream, it can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition where the body’s response to infection damages tissues and organs. Sepsis requires urgent medical intervention.
- Bone Infection: In advanced stages, an untreated abscess can infect the jawbone, leading to a condition called osteomyelitis. This can require surgical intervention and may cause long-term complications.
- Facial Cellulitis: The infection may spread to the soft tissues of the face, causing a condition called cellulitis. This can lead to difficulty swallowing, breathing, or opening your mouth, and may require antibiotics or surgical drainage.
It’s essential to seek dental care as soon as possible if you suspect that a tooth abscess is spreading. Early intervention can prevent the infection from reaching these dangerous stages and reduce the risk of more serious health complications.
Why Is a Tooth Abscess Dangerous for My Body?
A tooth abscess is not just a localised issue in your mouth—if left untreated, the infection can spread throughout your body, leading to serious health complications. The infection caused by a tooth abscess can affect much more than just your teeth and gums, which is why it’s essential to take action at the first sign of an abscess.
Risk of Infection Spreading
The bacteria from a tooth abscess can easily travel through your bloodstream or lymphatic system, spreading to other areas of your body. This is particularly concerning because the infection can move to critical areas, resulting in severe health conditions.

Potential Complications of a Tooth Abscess:
- Sepsis: One of the most serious risks of an untreated tooth abscess is sepsis, a life-threatening infection that can cause widespread inflammation throughout the body. Sepsis can result in organ failure, and without immediate treatment, it can be fatal. Early intervention with antibiotics and dental care is essential to prevent sepsis from developing.
- Heart Disease: There is a known connection between poor oral health and heart disease. Bacteria from a tooth abscess can enter the bloodstream and travel to the heart, potentially causing infections such as endocarditis (infection of the heart’s inner lining). This can increase the risk of heart failure and other cardiovascular issues, particularly in people with existing heart conditions.
- Jawbone Infection (Osteomyelitis): If the abscess continues to spread unchecked, it can infect the jawbone. Osteomyelitis is a bone infection that can lead to bone loss, severe pain, and even the need for surgical procedures to drain the infection. This is a rare but serious complication that underscores the importance of seeking timely treatment.
- Airway Obstruction: In severe cases, the infection can spread to the throat and cause swelling, which may lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing. This can become an emergency situation requiring immediate intervention.
Why Timely Treatment is Critical
The longer a tooth abscess goes untreated, the higher the risk of these complications. The good news is that abscesses are often treatable with antibiotics and dental procedures, such as draining the abscess or performing a root canal. If the infection spreads or causes irreversible damage, however, it may require more extensive treatments, including surgery.
By seeking prompt treatment for a tooth abscess, you not only protect your oral health but also your overall well-being. Ignoring the issue can put your body at risk and lead to complications that could have been prevented.
Can a Tooth Abscess Heal on Its Own?
While it is true that the body has a natural ability to fight infections, a tooth abscess generally cannot heal on its own without professional dental treatment. The infection at the root of the tooth, often caused by untreated decay or injury, requires specific care to ensure that the infection is properly addressed and to prevent further complications.
Why Professional Treatment is Essential
Although your immune system may attempt to combat the infection, a tooth abscess often continues to progress and may not resolve without proper intervention. The infection can spread deeper into the tooth, into the surrounding tissues, or even into the bloodstream, leading to more serious health problems. If left untreated, the infection can destroy the tooth, spread to other areas of the body, and result in permanent damage.
The Dangers of Self-Treating a Tooth Abscess
Some people may try to treat a tooth abscess at home by using over-the-counter pain relief, applying cold compresses, or even attempting to drain the abscess themselves. While these methods may offer temporary relief, they do not address the underlying infection and can make the problem worse. Self-treatment can lead to:
- Increased risk of infection spreading: Without draining the abscess properly or addressing the root cause, the infection may spread to other parts of your body, increasing the risk of serious complications like sepsis, heart disease, or jawbone infections.
- Improper drainage: Draining an abscess without professional help can introduce more bacteria, potentially worsening the infection and leading to further complications.
- Damage to surrounding tissues: Attempting to treat the abscess without proper care can harm the surrounding tissues, making it harder for your dentist to save the tooth and requiring more extensive treatment later.
What Treatment Is Required for an Abscess?
When dealing with a tooth abscess, it is crucial to seek professional dental care to ensure the infection is properly treated and complications are avoided. Depending on the severity and location of the abscess, various treatment options may be recommended to address the infection and preserve your dental health.
Common Treatments for a Tooth Abscess:
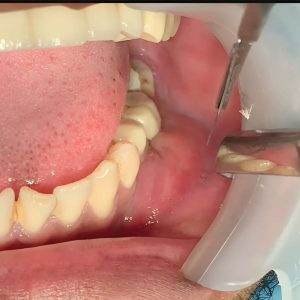
- Drainage: The primary goal in treating a tooth abscess is to drain the pus and alleviate the pressure. This may involve making a small incision in the gum or draining the abscess through the tooth itself. This procedure helps relieve pain and begins the healing process by removing the source of infection.
- Root Canal Therapy: If the infection has reached the pulp (soft tissue) of the tooth, a root canal may be necessary to remove the infected tissue. During this procedure, the dentist cleans and disinfects the root canals, then fills them with a special material to seal the tooth. Root canal therapy can save the tooth and restore its function, eliminating the infection from within.
- Antibiotics: In many cases, antibiotics are prescribed to help control the infection, especially if it has spread beyond the abscess or is causing significant swelling and fever. Antibiotics are typically used in conjunction with other treatments to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
- Tooth Extraction: If the infection is too severe and the tooth cannot be saved, the dentist may recommend extraction. This is typically a last resort when the tooth is beyond repair, and it helps prevent the infection from spreading further. After the extraction, your dentist will discuss options for replacing the missing tooth, such as implants, bridges, or dentures.
Why Seeing a Dentist Is Essential
It’s important to remember that attempting to treat a tooth abscess at home can worsen the situation. Professional dental care ensures the abscess is properly drained, the infection is eliminated, and the affected tooth is either saved or safely extracted.
Ignoring a tooth abscess or delaying treatment can lead to serious health risks, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body. By seeking prompt dental care, you can avoid complications, protect your overall health, and ensure your smile remains healthy for years to come.
Will Antibiotics Fix My Tooth?
While antibiotics are essential for managing the infection associated with a tooth abscess, they do not address the root cause of the problem. Antibiotics help control and reduce the spread of infection, especially when it has reached surrounding tissues or is causing systemic symptoms such as fever. However, antibiotics alone will not treat the abscess or eliminate the infection at the source.
The abscess itself is a result of a bacterial infection that has formed within the tooth or surrounding gum tissue. To fully resolve the issue and prevent the infection from returning, the underlying dental problem must be addressed. This could involve procedures such as draining the abscess, performing a root canal to remove infected tissue, or in some cases, extracting the tooth.
Relying on antibiotics without proper dental treatment can lead to the infection persisting or even worsening. Additionally, while antibiotics may temporarily alleviate symptoms like swelling and pain, they are not a long-term solution and cannot stop the infection from reoccurring.
It’s crucial to see a dentist for comprehensive treatment that tackles both the infection and the dental issue that caused it. This ensures that the abscess is fully treated, the infection is eliminated, and your oral health is restored.
How Do You Know If an Abscess Is Going Away?

As a tooth abscess heals, there are several key signs that indicate the infection is resolving. Monitoring these symptoms can help you determine whether the abscess is improving and if it’s on the path to recovery:
1. Decrease in Pain
One of the first signs that an abscess is healing is a noticeable decrease in pain. The throbbing and discomfort that initially accompany an abscess should lessen as the infection begins to resolve. The pain will become less intense and may eventually stop altogether.
2. Drainage Stops
If your abscess was draining pus or fluid, this should stop as the infection heals. The draining pus often decreases in volume and eventually ceases completely, signalling that the infection is being controlled. If the abscess was large, this could take a bit longer, but the drainage should reduce progressively.
3. Less Swelling
As the infection resolves, the swelling in the affected area will gradually subside. The redness and puffiness around the abscess will lessen, and the area will begin to look and feel more normal. Reduced swelling often indicates that the body’s immune system is effectively fighting off the infection.
4. Normal Tissue Appearance
The skin or gums around the abscess will return to their normal colour and texture. The redness and inflammation caused by the infection should fade, and the tissue should look healthy once again. If the abscess was on the gum, the gum tissue will appear more uniform, and the pimple-like bump may disappear.
While these signs are encouraging, it’s essential to remember that a tooth abscess should be properly treated by a dentist. If you notice improvement, it’s still important to follow through with your dental care plan to ensure complete healing and to prevent future issues. Always consult your dentist for advice on how to manage your abscess and monitor its progress effectively.
How Long Does It Take for an Abscess to Heal?
The healing time for a tooth abscess can vary depending on the severity of the infection, the type of abscess, and the treatment used. Generally, with proper dental care, most abscesses will begin to improve within a few days to a few weeks.
Typical Healing Timeline:
- Initial Healing: After receiving treatment, such as drainage, antibiotics, or a root canal, you should notice some relief within a few days. Pain and swelling often begin to decrease shortly after treatment begins.
- Complete Healing: For the infection to fully heal, it can take anywhere from one to three weeks. However, if more extensive treatment like tooth extraction is necessary, healing may take longer.
Factors Affecting Healing Time:

- Type of Abscess:
- A gingival abscess (located in the gum tissue) may heal faster compared to a periapical abscess (at the tooth root), which typically requires more intensive treatment.
- Periodontal abscesses, affecting the supporting structures of the tooth, may take longer to heal depending on the extent of the infection.
- Treatment Used:
- The type of treatment plays a significant role in how quickly the abscess heals. If antibiotics are prescribed, they will help manage the infection, but the infection itself may still take time to clear. More invasive treatments, such as root canals or drainage, may lead to quicker healing, although recovery may be longer if an extraction is necessary.
- Overall Health:
- Your immune system plays an important role in healing. People with a weakened immune system or underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, may experience longer recovery times.
- Abscess Size and Severity:
- Larger abscesses or those that have spread deeper into the tooth or surrounding tissues may take longer to heal. Abscesses that are caught and treated early often heal more quickly compared to those left untreated for longer periods.
Recognising the stages of a tooth abscess early on is crucial for effective treatment and preventing serious complications. Understanding the progression of the stages of a tooth abscess, from enamel decay to potential tooth loss, helps ensure you seek the right care at the right time. If you suspect you have a tooth abscess, it’s essential to seek dental care as soon as possible. Prompt action will help prevent the infection from spreading and ensure proper healing. Don’t delay in getting professional treatment, as timely care can save your tooth and protect your overall health.

